Heart Disease
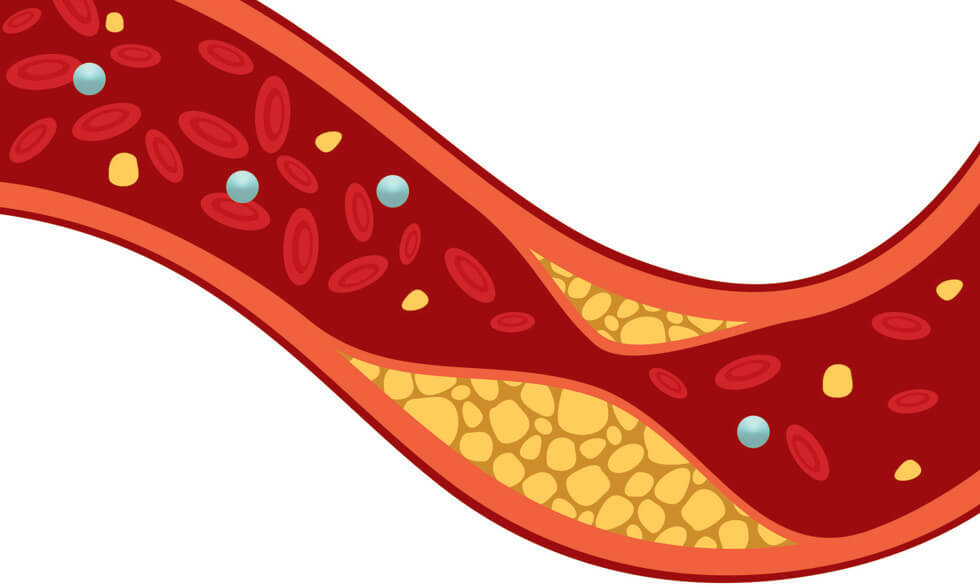
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) encompasses conditions affecting the heart and vascular system, including coronary artery disease (CAD), heart failure, and arrhythmias. Evidence-based nutritional interventions are integral to both primary prevention and secondary prevention strategies, working alongside pharmacological and lifestyle interventions to optimize cardiovascular outcomes.